Description logic
Description logic (DL) is a family of formal knowledge representation languages. It is more expressive than propositional logic but has more efficient decision problems than first-order predicate logic.
DL is used in artificial intelligence for formal reasoning on the concepts of an application domain (known as terminological knowledge). It is of particular importance in providing a logical formalism for ontologies and the Semantic Web. The most notable application outside information science is in bioinformatics where DL assists in the codification of medical knowledge.
Contents |
Introduction
A Description Logic (DL) models concepts, roles and individuals, and their relationships.
The fundamental modeling concept of a DL is the axiom - a logical statement relating roles and/or concepts.[1] This is a key difference from the frames paradigm where a frame specification declares and completely defines a class.[1]
Nomenclature
Differences from OWL
| OWL | DL |
|---|---|
| class | concept |
| property | role |
| object | individual |
Naming convention
There are many varieties of Description Logic and there is an informal naming convention, roughly describing the operators allowed. The expressivity is encoded in the label for a logic starting with one of the following basic logics:
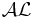 |
Attributive language. This is the base language which allows: |
|
|
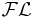 |
Frame based description language,[2] allows: |
|
|
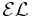 |
Allows: |
|
Followed by any of the following extensions:
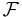 |
Functional properties. |
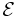 |
Full existential qualification (Existential restrictions that have fillers other than owl:Thing). |
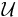 |
Concept union. |
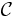 |
Complex concept negation. |
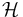 |
Role hierarchy (subproperties - rdfs:subPropertyOf). |
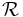 |
Limited complex role inclusion axioms; reflexivity and irreflexivity; role disjointness. |
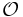 |
Nominals. (Enumerated classes of object value restrictions - owl:oneOf, owl:hasValue). |
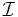 |
Inverse properties. |
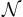 |
Cardinality restrictions (owl:cardinality, owl:maxCardinality). |
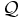 |
Qualified cardinality restrictions (available in OWL 2, cardinality restrictions that have fillers other than owl:Thing). |
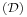 |
Use of datatype properties, data values or data types. |
Exceptions
Some canonical DLs that do not exactly fit this convention are:
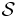 |
An abbreviation for 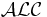 with transitive roles. with transitive roles. |
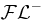 |
A sub-language of 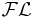 , which is obtained by disallowing role restriction. This is equivalent to , which is obtained by disallowing role restriction. This is equivalent to 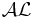 without atomic negation. without atomic negation. |
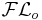 |
A sub-language of 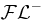 , which is obtained by disallowing limited existential quantification. , which is obtained by disallowing limited existential quantification. |
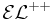 |
Alias for 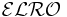 .[3] .[3] |
Examples
As an example, 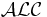 is a centrally important description logic from which comparisons with other varieties can be made.
is a centrally important description logic from which comparisons with other varieties can be made. 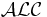 is simply
is simply 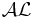 with complement of any concept allowed, not just atomic concepts.
with complement of any concept allowed, not just atomic concepts.
A further example, the description logic 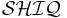 is the logic
is the logic 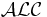 plus extended cardinality restrictions, and transitive and inverse roles. The naming conventions aren't purely systematic so that the logic
plus extended cardinality restrictions, and transitive and inverse roles. The naming conventions aren't purely systematic so that the logic 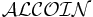 might be referred to as
might be referred to as 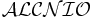 and abbreviations are made where possible,
and abbreviations are made where possible, 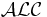 is used instead of the equivalent
is used instead of the equivalent 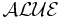 .
.
The Protégé ontology editor supports 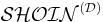 . Three major bioinformatic terminology bases, Snomed, Galen, and GO, are expressible in
. Three major bioinformatic terminology bases, Snomed, Galen, and GO, are expressible in  (with additional role properties).
(with additional role properties).
OWL 2 provides the expressiveness of 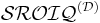 , OWL-DL is based on
, OWL-DL is based on 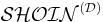 , and for OWL-Lite it is
, and for OWL-Lite it is 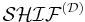 .
.
History
Description logic (DL) was given its current name in the 1980s. Previous to this it was called (chronologically): terminological systems, and concept languages.
Knowledge representation
Frames and semantic networks lack formal (logic-based) semantics.[4] DL was first introduced into Knowledge Representation (KR) systems to overcome this deficiency.[4]
The first DL-based KR system was KL-ONE (by Ronald J. Brachman and Schmolze, 1985). During the '80s other DL-based systems using structural subsumption algorithms[4] were developed including KRYPTON (1983), LOOM (1987), BACK (1988), K-REP (1991) and CLASSIC (1991). This approach featured DL with limited expressiveness but relatively efficient (polynomial time) reasoning.[4]
In the early '90s, the introduction of a new tableau based algorithm paradigm allowed efficient reasoning on more expressive DL.[4] DL-based systems using these algorithms - such as KRIS (1991) - show acceptable reasoning performance on typical inference problems even though the worst case complexity is no longer polynomial.[4]
From the mid '90s, reasoners were created with good practical performance on very expressive DL with high worst case complexity.[4] Examples from this period include FaCT,[5] RACER (2001), CEL (2005), and KAON 2 (2005).
DL reasoners, such as FaCT, FaCT++,[5] RACER, DLP and Pellet,[6] implement the analytic tableau method. KAON2 is implemented by algorithms which reduce a SHIQ(D) knowledge base to a disjunctive datalog program.
Semantic Web
The DARPA Agent Markup Language (DAML) and Ontology Inference Layer (OIL) ontology languages for the semantic web can be viewed as syntactic variants of DL.[7] In particular, the formal semantics and reasoning in OIL use the 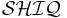 DL.[8] The DAML+OIL DL was developed as a submission to[9] - and formed the starting point of - the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) Web Ontology Working Group.[10] In 2004, the Web Ontology Working Group completed its work by issuing the OWL[11] recommendation. The design of OWL is based on the
DL.[8] The DAML+OIL DL was developed as a submission to[9] - and formed the starting point of - the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) Web Ontology Working Group.[10] In 2004, the Web Ontology Working Group completed its work by issuing the OWL[11] recommendation. The design of OWL is based on the 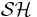 family of DL[12] with OWL DL and OWL Lite based on
family of DL[12] with OWL DL and OWL Lite based on 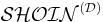 and
and 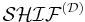 respectively.[12]
respectively.[12]
The W3C OWL Working Group began work in 2007 on a refinement of - and extension to - OWL.[13] In 2009, this was completed by the issuance of the OWL2 recommendation.[14] OWL2 is based on the description logic 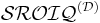 .[15] Practical experience demonstrated that OWL DL lacked several key features necessary to model complex domains.[1]
.[15] Practical experience demonstrated that OWL DL lacked several key features necessary to model complex domains.[1]
Modeling
In DL, a distinction is drawn between the so-called TBox (terminological box) and the ABox (assertional box). In general, the TBox contains sentences describing concept hierarchies (i.e., relations between concepts) while the ABox contains ground sentences stating where in the hierarchy individuals belong (i.e., relations between individuals and concepts). For example, the statement:
(1) Every employee is a person
belongs in the TBox, while the statement:
(2) Bob is an employee
belongs in the ABox.
Note that the TBox/ABox distinction is not significant, in the same sense that the two "kinds" of sentences are not treated differently in first-order logic (which subsumes most DL). When translated into first-order logic, a subsumption axiom like (1) is simply a conditional restriction to unary predicates (concepts) with only variables appearing in it. Clearly, a sentence of this form is not privileged or special over sentences in which only constants ("grounded" values) appear like (2).
So why was the distinction introduced? The primary reason is that the separation can be useful when describing and formulating decision-procedures for various DL. For example, a reasoner might process the TBox and ABox separately, in part because certain key inference problems are tied to one but not the other one ('classification' is related to the TBox, 'instance checking' to the ABox). Another example is that the complexity of the TBox can greatly affect the performance of a given decision-procedure for a certain DL, independently of the ABox. Thus, it is useful to have a way to talk about that specific part of the knowledge base.
The secondary reason is that the distinction can make sense from the knowledge base modeler's perspective. It is plausible to distinguish between our conception of terms/concepts in the world (class axioms in the TBox) and particular manifestations of those terms/concepts (instance assertions in the ABox). In the above example: when the hierarchy within a company is the same in every branch but the assignment to employees is different in every department (because there are other people working there), this distinction makes sense to reuse the TBox for different branches.
There are two features of Description Logic that are not shared by most other data description formalisms: DL does not make the Unique Name Assumption (UNA) or the Closed World Assumption (CWA). Not having UNA means that two concepts with different names may be allowed by some inference to be shown to be equivalent. Not having CWA, or rather having the Open World Assumption (OWA) means that lack of knowledge of a fact does not immediately imply knowledge of the negation of a fact.
Formal description
Like first order logic (FOL), a syntax defines which collections of symbols are legal expressions in a Description Logic (DL), and semantics determine meaning. Unlike FOL, a DL may have several well known syntactic variants.[7]
Syntax
The syntax of a member of the description logic family is characterized by its recursive definition, in which the constructors that can be used to form concept terms are stated. Some constructors are related to logical constructors in first-order logic (FOL) such as intersection or conjunction of concepts, union or disjunction of concepts, negation or complement of concepts, universal restriction and existential restriction. Other constructors have no corresponding construction in FOL including restrictions on roles for example, inverse, transitivity and functionality.
Notation
Let C and D be concepts, a and b be individuals, and R be a role.
| Symbol | Description | Example | Read |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
all concept names |  |
top |
 |
empty concept |  |
bottom |
 |
intersection or conjunction of concepts | 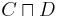 |
C and D |
 |
union or disjunction of concepts |  |
C or D |
 |
negation or complement of concepts | 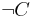 |
not C |
 |
universal restriction | 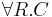 |
all R-successors are in C |
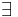 |
existential restriction | 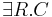 |
an R-successor exists in C |
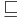 |
Concept inclusion |  |
all C are D |
 |
Concept equivalence | 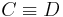 |
C is equivalent to D |
 |
Concept definition | 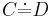 |
C is defined to be equal to D |
 |
Concept assertion | 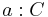 |
a is a C |
 |
Role assertion | 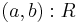 |
a is R-related to b |
The description logic ALC
The prototypical DL Attributive Concept Language with Complements (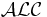 ) was introduced by Manfred Schmidt-Schauß and Gert Smolka in 1991, and is the basis of many more expressive DL.[4] The following definitions follow the treatment in Baader et al.[4]
) was introduced by Manfred Schmidt-Schauß and Gert Smolka in 1991, and is the basis of many more expressive DL.[4] The following definitions follow the treatment in Baader et al.[4]
Let 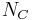 ,
, 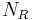 and
and 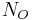 be (respectively) sets of concept names (also known as atomic concepts), role names and individual names (also known as individuals, nominals or objects). Then the ordered triple (
be (respectively) sets of concept names (also known as atomic concepts), role names and individual names (also known as individuals, nominals or objects). Then the ordered triple (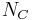 ,
, 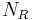 ,
, 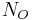 ) is the signature.
) is the signature.
Concepts
The set of 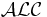 concepts is the smallest set such that:
concepts is the smallest set such that:
- The following are concepts:
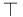 (top is a concept)
(top is a concept) (bottom is a concept)
(bottom is a concept)- Every
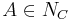 (all atomic concepts are concepts)
(all atomic concepts are concepts)
- If
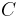 and
and 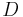 are concepts and
are concepts and 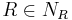 then the following are concepts:
then the following are concepts:
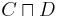 (the intersection of two concepts is a concept)
(the intersection of two concepts is a concept) (the union of two concepts is a concept)
(the union of two concepts is a concept)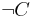 (the complement of a concept is a concept)
(the complement of a concept is a concept)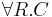 (the universal restriction of a concept by a role is a concept)
(the universal restriction of a concept by a role is a concept)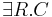 (the existential restriction of a concept by a role is a concept)
(the existential restriction of a concept by a role is a concept)
Terminological axioms
A general concept inclusion (GCI) has the form  where
where 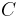 and
and 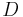 are concepts. Write
are concepts. Write 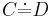 when
when  and
and  . A TBox is any finite set of GCIs.
. A TBox is any finite set of GCIs.
Assertional axioms
- A concept assertion is a statement of the form
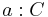 where
where 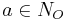 and C is a concept.
and C is a concept. - A role assertion is a statement of the form
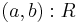 where
where 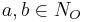 and R is a role.
and R is a role.
An ABox is a finite set of assertional axioms.
Knowledge base
A knowledge base (KB) is an ordered pair 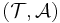 for TBox
for TBox 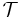 and ABox
and ABox 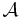 .
.
Semantics
The semantics of description logic are defined by interpreting concepts as sets of individuals and roles as sets of pairs of individuals. Those individuals are typically assumed from a given domain. The semantics of non atomic concepts and roles is then defined in terms of atomic concepts and roles. This is done by using a recursive definition similar to the syntax.
The description logic ALC
The following definitions follow the treatment in Baader et al.[4]
A terminological interpretation 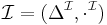 over a signature
over a signature 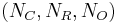 consists of
consists of
- a non-empty set
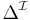 called the domain
called the domain - a interpretation function
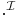 that maps:
that maps:
- every individual
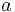 to an element
to an element 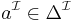
- every concept to a subset of
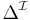
- every role name to a subset of
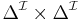
- every individual
such that
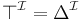
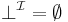
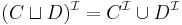 (union means disjunction)
(union means disjunction)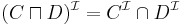 (intersection means conjunction)
(intersection means conjunction)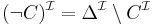 (complement means negation)
(complement means negation)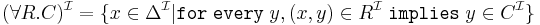
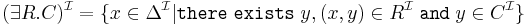
Define 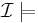 (read I models) as follows
(read I models) as follows
TBox
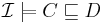 if and only if
if and only if 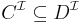
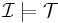 if and only if
if and only if 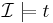 for every
for every 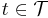
ABox
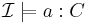 if and only if
if and only if 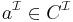
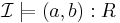 if and only if
if and only if 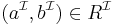
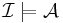 if and only if
if and only if 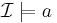 for every
for every 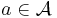
Knowledge base
Let 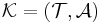 be a knowledge base.
be a knowledge base.
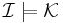 if and only if
if and only if 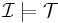 and
and 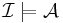
Inference
Decision problems
In addition to the ability to describe concepts formally, one also would like to employ the description of a set of concepts to ask questions about the concepts and instances described. The most common decision problems are basic database-query-like questions like instance checking (is a particular instance (member of an A-box) a member of a given concept) and relation checking (does a relation/role hold between two instances, in other words does a have property b), and the more global-database-questions like subsumption (is a concept a subset of another concept), and concept consistency (is there no contradiction among the definitions or chain of definitions). The more operators one includes in a logic and the more complicated the T-box (having cycles, allowing non-atomic concepts to include each other), usually the higher the computational complexity is for each of these problems (see Navigator on Description Logic Complexity for examples).
Relationship with other logic
First order logic
Many Description Logic models (DLs) are decidable fragments of first order logic (FOL).[4] Some DLs now include operations (for example, transitive closure of roles) that allow efficient inference but cannot be expressed in FOL.[4]
Fuzzy description logic
Fuzzy description logic combines fuzzy logic with DLs. Since many concepts that are needed for intelligent systems lack well defined boundaries, or precisely defined criteria of membership, fuzzy logic is needed to deal with notions of vagueness and imprecision. This offers a motivation for a generalization of description logic towards dealing with imprecise and vague concepts.
What people should also think about for intelligent systems is multiple viewpoints of the data. This will lead to subjective (as opposed to objective) intelligent systems.
Modal logic
Description Logic is related to — but developed independently of — modal logic (ML).[4] Many - but not all - DL are syntactic variants of ML.[4]
Examples
| DL | ML |
|---|---|
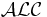 |
K[4] |
Temporal description logic
Temporal description logic represents - and allow reasoning about - time dependent concepts and many different approaches to this problem exist.[16] For example, a description logic might be combined with a modal temporal logic such as Linear temporal logic.
See also
Notes
- ^ a b c Grau, B.; Horrocks, I.; Motik, B.; Parsia, B.; Patelschneider, P.; Sattler, U. (2008). "OWL 2: The next step for OWL". Web Semantics: Science, Services and Agents on the World Wide Web 6 (4): 309–322. doi:10.1016/j.websem.2008.05.001.
- ^ Levesque, Hector J.; Brachmann, Ronald J. (1987). "Expressiveness and tractability in knowledge representation and reasoning". Computational Intelligence (3).
- ^ Maier, Frederick; Mutharaju, Raghava; Hitzler, Pascal (2010). "Distributed Reasoning with EL++ Using MapReduce". Technical Report, Kno.e.sis Center, Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio. http://knoesis.wright.edu/faculty/pascal/resources/publications/elpp-mapreduce2010.pdf. Retrieved 2011-12-25.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Franz Baader, Ian Horrocks, and Ulrike Sattler Chapter 3 Description Logics. In Frank van Harmelen, Vladimir Lifschitz, and Bruce Porter, editors, Handbook of Knowledge Representation. Elsevier, 2007.
- ^ a b Tsarkov, D.; Horrocks, I. (2006). "FaCT++ Description Logic Reasoner: System Description". Automated Reasoning. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 4130. pp. 292–297. doi:10.1007/11814771_26. ISBN 978-3-540-37187-8. http://www.cs.ox.ac.uk/ian.horrocks/Publications/download/2006/TsHo06a.pdf.
- ^ Sirin, E.; Parsia, B.; Grau, B.; Kalyanpur, A.; Katz, Y. (2007). "Pellet: A practical OWL-DL reasoner". Web Semantics: Science, Services and Agents on the World Wide Web 5 (2): 51–53. doi:10.1016/j.websem.2007.03.004. http://pellet.owldl.com/papers/sirin05pellet.pdf.
- ^ a b Ian Horrocks and Ulrike Sattler Ontology Reasoning in the SHOQ(D) Description Logic, in Proceedings of the Seventeenth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2001.
- ^ Fensel, D.; Van Harmelen, F.; Horrocks, I.; McGuinness, D. L.; Patel-Schneider, P. F. (2001). "OIL: An ontology infrastructure for the Semantic Web". IEEE Intelligent Systems 16 (2): 38–45. doi:10.1109/5254.920598.
- ^ Ian Horrocks and Peter F. Patel-Schneider The Generation of DAML+OIL. In Proceedings of the 2001 Description Logic Workshop (DL 2001), volume 49 of CEUR <http://ceur-ws.org/>, pages 30–35, 2001.
- ^ Web Ontology Working Group Charter, 2003
- ^ W3C Press Release, 2004
- ^ a b Horrocks, I. (2003). "From SHIQ and RDF to OWL: The making of a Web Ontology Language". Web Semantics: Science, Services and Agents on the World Wide Web 1: 7–26. doi:10.1016/j.websem.2003.07.001. http://www.comlab.ox.ac.uk/people/ian.horrocks/Publications/download/2003/HoPH03a.pdf.
- ^ OWL Working Group Charter, 2007
- ^ Hitzler, Pascal; Krötzsch, Markus; Parsia, Bijan; Patel-Schneider, Peter F.; Rudolph, Sebastian (27 October 2009). "OWL 2 Web Ontology Language Primer". OWL 2 Web Ontology Language. World Wide Wed Consortium. http://www.w3.org/TR/2009/REC-owl2-primer-20091027/. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ Pascal Hitzler, Markus Krötzsch, Sebastian Rudolph (August 25, 2009). Foundations of Semantic Web Technologies. CRCPress. ISBN 142009050X. http://www.semantic-web-book.org.
- ^ Alessandro Artale and Enrico Franconi "Temporal Description Logics". In "Handbook of Temporal Reasoning in Artificial Intelligence", 2005.
References
- F. Baader, D. Calvanese, D. L. McGuinness, D. Nardi, P. F. Patel-Schneider: The Description Logic Handbook: Theory, Implementation, Applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2003. ISBN 0-521-78176-0
- Ian Horrocks, Ulrike Sattler: Ontology Reasoning in the SHOQ(D) Description Logic, in Proceedings of the Seventeenth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2001.
- D. Fensel, F. van Harmelen, I. Horrocks, D. McGuinness, and P. F. Patel-Schneider: OIL: An Ontology Infrastructure for the Semantic Web. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 16(2):38-45, 2001.
- Ian Horrocks and Peter F. Patel-Schneider: The Generation of DAML+OIL. In Proceedings of the 2001 Description Logic Workshop (DL 2001), volume 49 of CEUR <http://ceur-ws.org/>, pages 30–35, 2001.
- Ian Horrocks, Peter F. Patel-Schneider, and Frank van Harmelen: From SHIQ and RDF to OWL: The Making of a Web Ontology Language. Journal of Web Semantics, 1(1):7-26, 2003.
- Bernardo Cuenca Grau, Ian Horrocks, Boris Motik, Bijan Parsia, Peter Patel-Schneider, and Ulrike Sattler: OWL 2: The next step for OWL. Journal of Web Semantics, 6(4):309-322, November 2008.
- Franz Baader, Ian Horrocks, and Ulrike Sattler: Chapter 3 Description Logics. In Frank van Harmelen, Vladimir Lifschitz, and Bruce Porter, editors, Handbook of Knowledge Representation. Elsevier, 2007.
- Alessandro Artale and Enrico Franconi: Temporal Description Logics. In Handbook of Temporal Reasoning in Artificial Intelligence, 2005.
- Web Ontology (WebONT) Working Group Charter. W3C, 2003
- World Wide Web Consortium Issues RDF and OWL Recommendations. Press Release. W3C, 2004.
- OWL Working Group Charter. W3C, 2007.
- OWL 2 Connects the Web of Knowledge with the Web of Data. Press Release. W3C, 2009.
Further reading
- Ontologies and the Semantic Web by Ian Horrocks. Communications of the ACM, 51(12):58-67, December 2008.
- Description Logics by Franz Baader. In Reasoning Web: Semantic Technologies for Information Systems, 5th International Summer School 2009.
- From SHIQ and RDF to OWL: The Making of a Web Ontology Language by Ian Horrocks, Peter F. Patel-Schneider, and Frank van Harmelen. Journal of Web Semantics, 1(1):7-26, 2003.
- OWL 2: The next step for OWL by Bernardo Cuenca Grau, Ian Horrocks, Boris Motik, Bijan Parsia, Peter Patel-Schneider, and Ulrike Sattler. Journal of Web Semantics, 6(4):309-322, November 2008.
- Introduction to Description Logics by Enrico Franconi, Faculty of Computer Science, Free University of Bolzano, Italy
- Description Logics - The Marriage of Logic and Objects
External links
- Description Logics, the official web page of the community
- Navigator on Description Logic Complexity at the University of Manchester
- A list of DL reasoners at the University of Manchester
Tools
- Reasoners
There are some reasoners that deal with OWL and Description Logic. These are some of the most popular:
- CEL is a free (for non-commercial use) LISP-based reasoner
- Cerebra Engine was a commercial C++-based reasoner, acquired in 2006 by webMethods.
- FaCT++ is a free open-source C++-based reasoner.
- KAON2 is a free (free for non-commercial usage) Java reasoner.
- MSPASS is a free open-source C reasoner for numerous description logic models.
- Pellet is a dual-licensed (AGPL and proprietary) commercial, Java-based reasoner.
- RacerPro of Racer Systems is a commercial (free trials and research licenses are available) lisp-based reasoner.
- Sim-DL is a free open-source Java-based reasoner for the language ALCHQ. It also provides a similarity measurement functionality between concepts. To access this functionality a Protégé plugin can be used.
- HermiT is an open source reasoner based on the hypertableaux calculus. It is developed by the University of Oxford.
- Editors
- Protégé is a free, open source ontology editor and knowledge-base framework, which can use DL reasoners which offer a DIG interface as backends for consistency checks.
- SWOOP is an open source ontology editor originally developed at the University of Maryland.
- Interfaces
- DIG Implementation. DIG is an XML interface to DL systems, recommended by the DL Implementation Group. DIG 2.0 is an ongoing effort for a new DIG interface standard.
- OWL API is an open source Java interface to the W3C Web Ontology Language OWL developed by the University Of Manchester
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||